-
Software Development Engineer in Test (SDET) Resume Example
-
Automation Test Engineer Resume Example
-
Senior Software Quality Assurance (SQA) Engineer Resume Example
-
Senior Software Development Engineer in Test (SDET Resume Example)
-
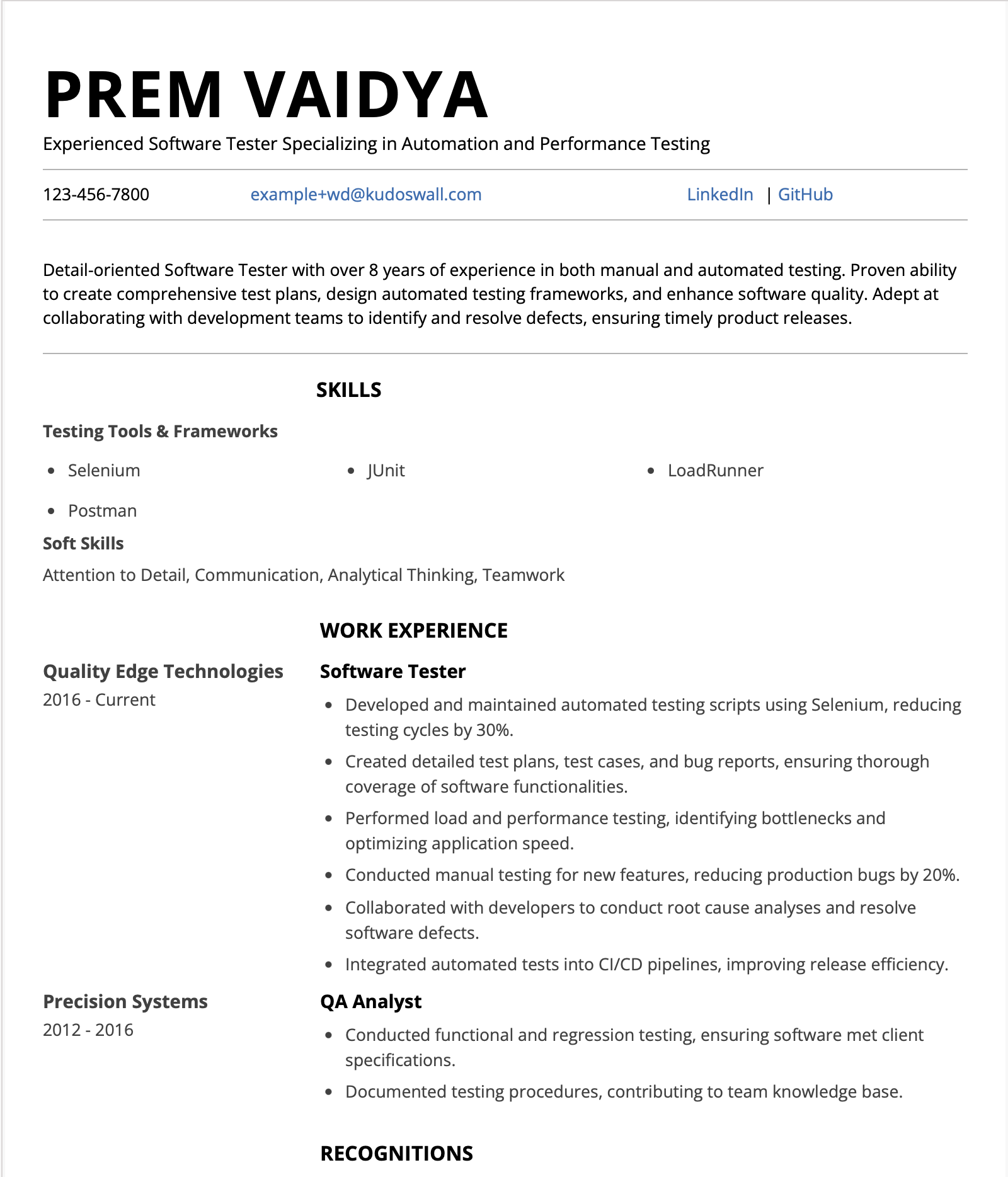
Experienced Software Tester Resume Example Resume Example
-
Software Tester - Fresher Resume Example
Expert Career Advice for QA Engineers
Stay ahead in the fast-paced world of software quality assurance and testing with expert career insights. Learn how to write a standout SQA or SDET resume, optimize your LinkedIn profile for maximum visibility, and craft persuasive cover letters that will set you apart from the competition in the QA industry.
Optimize Your Resume with the Right QA Test Keywords
To get noticed by recruiters and Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS), your resume must include the right QA test keywords. These keywords highlight your expertise in software testing and increase your chances of landing a top-quality assurance job.
Essential QA Test Keywords for Your Resume
- QA test automation
- Manual testing
- Test case development
- Bug tracking
- Regression testing
- Performance testing
- API testing
- Security testing
- Load testing
- Agile testing
- Selenium, Cypress, Appium
- Test management tools (JIRA, TestRail, ALM)
Where to Use QA Test Keywords in Your Resume
Strategically placing QA test keywords in your resume can improve visibility and ranking in ATS.
- Resume Summary: "Experienced QA Engineer with expertise in test automation and performance testing."
- Skills Section: List essential QA skills like API testing, regression testing, and automation tools.
- Work Experience: "Led a team in implementing automated test cases using Selenium and JIRA."
Where to Use QA Test Keywords in Your Cover Letter
Just like in your resume, using QA test keywords in your cover letter helps demonstrate expertise and relevance to recruiters.
- Opening Paragraph: Mention your expertise in manual testing, test automation, and performance testing.
- Body: Highlight your experience with Selenium, API testing, and Agile methodologies to showcase skills.
- Closing Statement: Reinforce your proficiency in QA test automation and bug tracking to leave a strong impression.
Check If Your Resume is ATS-Friendly
Want to see how well your resume ranks for **QA test keywords**? Use our ATS Resume Checker to analyze and optimize your resume instantly.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the role of an SDET (Software Development Engineer in Test)?
An SDET, or Software Development Engineer in Test, combines software development and testing skills. They design, write, and execute automated tests to ensure high software quality. SDETs often work closely with developers and may contribute to building testing frameworks, writing code, and performing detailed code reviews.
2. What skills should I include in a QA Engineer resume?
A QA Engineer resume should emphasize skills such as test automation, manual testing, knowledge of QA methodologies, proficiency with testing tools (e.g., Selenium, JIRA), scripting languages (e.g., Python, JavaScript), bug tracking, and strong analytical thinking.
3. What is the difference between a QA Tester and a Software Tester?
A QA Tester focuses on testing the quality of software throughout the software development lifecycle, often including manual and automated testing. A Software Tester primarily focuses on testing the functionality of software applications, ensuring they meet user requirements and perform as expected.
4. Should I highlight manual testing skills on my SQA resume?
Yes, if you have strong experience in manual testing, it is valuable to include it. Manual testing remains crucial for exploratory testing, UI testing, and scenarios where automation may not be practical or cost-effective. Pairing manual testing with automation skills can enhance your appeal to employers.
5. What certifications are beneficial for a QA Automation Engineer?
Certifications like the ISTQB (International Software Testing Qualifications Board), Certified Agile Tester (CAT), and specific automation tool certifications (e.g., Selenium, Cypress) are valuable for QA Automation Engineers. They demonstrate expertise and commitment to continuous learning.
6. What are the best automation tools for QA and testing?
Popular automation tools for QA include Selenium, Cypress, JIRA, TestNG, Appium (for mobile testing), and Cucumber (for behavior-driven development). Selecting the right tool depends on your project’s requirements and the technologies being used.
7. What methodologies should a QA Engineer be familiar with?
A QA Engineer should be familiar with methodologies like Agile, Scrum, Waterfall, DevOps practices, and Test-Driven Development (TDD) or Behavior-Driven Development (BDD). Understanding these methodologies helps ensure software testing aligns with the project’s development cycle.
8. What is manual testing, and when is it used?
Manual testing involves testing software manually to identify bugs and ensure software functionality. It is often used for exploratory testing, user interface testing, and when test cases require human judgment. Manual testing is valuable when automation is impractical or not cost-effective.
9. How can I highlight automation experience on my QA resume?
To emphasize automation experience, include details about automation tools you have used (e.g., Selenium, Appium), describe frameworks you have built, and provide specific examples of how your automation work reduced testing time or improved software quality.
10. What is quality assurance in software testing?
Quality assurance (QA) in software testing ensures that software meets specified standards and requirements. It involves setting quality guidelines, conducting tests, and ensuring software functionality, performance, and reliability align with business goals and user needs.
11. What is the role of a Quality Assurance Automation Engineer?
A Quality Assurance Automation Engineer designs, develops, and executes automated tests to ensure software functionality and performance. They create testing frameworks, write scripts, and work closely with developers to integrate automation into the software development lifecycle.
12. Can manual testers transition to QA automation roles?
Yes, manual testers can transition to QA automation roles by learning programming languages (e.g., Python, Java), understanding automation frameworks, and gaining hands-on experience with automation tools. Building expertise in automation can open more career opportunities.
13. What does SQA stand for?
SQA stands for Software Quality Assurance. It involves ensuring that software meets predefined standards for functionality, reliability, and performance through systematic testing and quality control processes.
14. How do I tailor my SQA resume for a specific job?
To tailor your SQA resume, carefully read the job description and highlight your relevant skills, tools, and methodologies used in testing. Mention key projects and any specific achievements that align with the role’s requirements.